What is Camber in road construction is a common question in civil engineering so In this civil experience article, we explain Camber in brief also why we provide camber, Type of Camber in Road with Advantages of Camber in Road, Objectives, Types of Camber, Types of Camber, IRC recommendation, Calculation camber formula, etc so read the whole article without skip and don’t forget to join and share if you gain some valuable solution from Civil Experience.
What is Camber in Road?
In real life, we always found in the road or highways the center part of the road surface is elevated with regards to the edges. This road slope from the diagonal direction of pavement is known as the Camber in Road.
The main purpose of camber in the road is to drain out the rainwater from the road surface around the edges of the pavement.
Camber in road construction is the slope provided to the road surface in the transverse direction to drain out the rainwater out of the road surface. Which is also known as the cross slope of the road.
The pavement design measurement of cambers are primarily based on the type of pavement and also on the average amount of rainfall in that area.
The rate of camber for road is generally indicated by 1:n ( 1 in n ) (1 vertical to n horizontal) or in proportions as n % (for instance, 1 in 50 or 2 %).
But they’re not recommended since they will wear down the surface. Generally, cambers of slope 2 to 3% are arranged as per IRC guidelines.
On straight roads, they’re shoulders with higher cross fall relating to that of the carriageway by 0.5%.
Uses of Camber in Road
Why camber is provided in the road and their Objectives of Camber in Road Pavement list are provided below
Camber in the road is provided for:
- Steep cambers are useful for eliminating surface water.
- To protect the road element by eliminating the entry of surface water to the subgrade soil through the road pavement.
- To drain off or remove rainwater from the surface of the pavement.
- To block the access of water into the layer of bitumen. (To avoid surface water entry to the bituminous pavement layers)
- To prevent water entrance to the subgrade of the road.
- To drain the rainwater from the pavement surface as fast as possible and to allow the pavement to get dry soon after the rain in the area.
- For quick drying of the road surface after rainfall, to avoid accidents due to skidding.
- To assure the quality performance and durability of the road.
Types of Camber in Road
- Composite camber
- Straight Camber or Sloped Camber
- Two Straight Line Camber
- Parabolic Camber
- Barrel camber
#1 Composite Camber
Composite camber in road design might be composed of partly straight & partly parabola lines or two straight lines having different slopes.
Generally, the central part of the road is made parabolic and provided with straight slopes near edges. This helps to decrease in intensity of pressure by increasing the contact area of the wheel.
#2 Straight Camber or Sloped Camber
This type of camber in the road is provided by meeting two straight surfaces in the crown. The Crown is the central and topmost point on the surface of the road.
The edge shape produces inconvenience to the traffic, so it isn’t used in general.
If w is the width of the pavement, n is the camber and R is the difference of level between edge and crown,
tantheta= R/W
n=tantheta=R/(W/2)
Also, tantheta=Y/X
or, Y/X=R/(W/2)=n
Hence, Y=nX
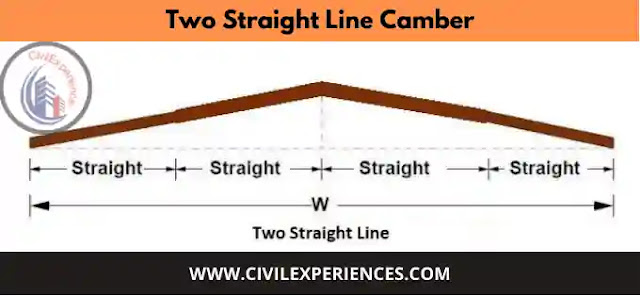
#3 Two Straight Line Camber
It consists of both straight lines steeper near the edges and flatters near the crown. This type of camber is considered to be the best for Indian roads.
#4 Parabolic Camber
In parabolic camber, the cross slope is in the shape of a simple quadratic parabola. In this case, the ordinate Y varies as the square of abscissa X (simple parabola equation).
Parabolic Camber of road formula give below is also known as camber in concrete road.
Y/X^2 = R/(W/2)^2
Y/X^2 = 4R/W^2
∴Y= (4R/W^2) / (X^2) = {(2ast2R)/(W ast W)} X^2
Y={2R/(WastW/2) }X^2=(2n/W)X^2
∴Y=(2n/W) X^2
Parabolic cambers are designed for fast-moving highways. A favorable condition for overtaking operation is provided due to the curved cross slope. As the slope increases outward to the road edge, the flow of surface water away from the pavement is enhanced. One disadvantage of parabolic cambers is that they are very difficult to construct.
#5 Barrel Camber
It consists of a continuous curve, either parabolic or elliptical. This type of camber is preferred for roads used by fast-moving vehicles.
Advantages of Camber in Road
This prevents rainwater to accumulate at local shrinkages or depressions and forming water pools around the road surface that are disagreeable to the public as well as to the road structure.
Camber provides quick drainage of rainwater and so saves the foundation course of this road structure from weakening from the percolation of rainwater to it through the road surface.
Method of Providing Camber in Road
Normally, the camber is provided on the straight roads by raising the center of the carriageway with respect to these edges, forming a crown or highest point on the center-line.
At horizontal curves with superelevation, the surface drainage is affected by raising the outer edge of the pavement with respect to the inner edge while providing this desired superelevation.
The rate of camber or cross slope is generally designed by 1 in n, which means the transverse slope is at a ratio of 1 vertical to”n” horizontal. Camber can be expressed in percentage. If the camber is n%, the cross slope is n in 100.
IRC Recommended Road Camber for Different Road Surface
As per IRC Recommended Road Camber for Different Road Surface How to calculate camber percentage in road (camber board in road construction).
| Sr. No. | Type of Road Surface | Range of Camber in Areas of | |
| Low Rainfall | Heavy Rainfall | ||
| 1 | Cement concrete and thick bituminous surface | 1 in 60 or 1.7% | 1 in 50 or 2.0% |
| 2 | Thin bituminous surface | 1 in 50 or 2.0% | 1 in 40 or 2.5% |
| 3 | Water bound macadam and gravel pavement | 1 in 40 or 2.5% | 1 in 33 or 3.0% |
| 4 | Earth Road | 1 in 33 or 3.0% | 1 in 25 or 4.0% |
Calculation of Camber in Road
How to calculate camber in road now come in your mind and here in Civil Experience we provide best solution for your every problem regarding Camber in Road.
Please share with friends and help them and don’t forget to join us for more civil engineering online learning.
By straight edge method
Camber of road formula calculation By straight edge method
Suppose Carriageway width is 3 meter
half-width = 1.5 meter
Considering Value of N = 6 cm or 0.06
Camber = 0.06/1.5×100 = 4% or 1:25
By Level Method
Camber of road formula calculation by By Level Method as follow
RL of LHS = 98.60 m
RL of Centre = 98.620
RL of LHS = 98.55
Average of LHS and RHS RL = 98.575
Difference of Level = 98.620 – 98.575 = 0.045
Camber = 0.045/1.5×100 = 3% or 1:33
Disadvantages of Providing Excessive Road Camber Height
- The road will wear and tear on the edges.
- It reduces the road width as everyone will try to move in the middle of the road.
- Chances of accidents will increase.
- The passengers feel unbalanced and discomfort during the journey.
FAQ 1: What is Camber in Road?
In the road or highways the center part of the road surface is elevated with regards to the edges. This road slope from the diagonal direction of pavement is known as the Camber in Road.
FAQ 2: What are the Uses of Camber in Road?
1. Steep cambers are useful for eliminating surface water. 2. To protect the road element by eliminating the entry of surface water to the subgrade soil through the road pavement. 3. To drain off or remove rainwater from the surface of the pavement. 4. To block the access of water into the layer of bitumen. (To avoid surface water entry to the bituminous pavement layers). 5. To prevent water entrance to the subgrade of the road. 6. To drain the rainwater from the pavement surface as fast as possible and to allow the pavement to get dry soon after the rain in the area. 7. For quick drying of the road surface after rainfall, to avoid accidents due to skidding. 8. To assure the quality performance and durability of the road.
FAQ 3: How many Types of Camber in Road?
1. Composite camber, 2. Straight Camber or Sloped Camber, 3. Two Straight Line Camber, 4. Parabolic Camber, 5. Barrel camber…
FAQ 4: What are the Advantages of Camber in Road?
This prevents rainwater to accumulate at local shrinkages or depressions and forming water pools around the road surface that are disagreeable to the public as well as to the road structure.Camber provides quick drainage of rainwater and so saves the foundation course of this road structure from weakening from the percolation of rainwater to it through the road surface.
FAQ 5: How many methord are available for Calculation of Camber in Road?
1. By straight edge method, 2. By Level Method…